RECTGEN
Analysis of Rectangular and Ridged Waveguide Structures
Applications Of RECTGEN
RECTGEN extends the application of rectangular modes in waveguide to several rectangular waveguide segments. The structure to be analysed is modelled as a number of discrete rectangular or ridged waveguide segments supporting propagating as well as evanescent modes. Multiple waveguide aperture segments can coexist side by side. This flexibility extends the scope of the analysis software to include many waveguide network structures. In order to achieve an optimal run-time, modes within waveguide segments can be selected in a flexible manner and various symmetry conditions can be applied. Typical components (Figure 1) are
- Symmetric and asymmetric rectangular waveguide tapers (may be overmoded) and step transformers.
- Multimode rectangular horn radiators.
- Rectangular corrugated horn radiators (radial corrugations also supported).
- Corrugated filters and polarisers.
- Multi-post and multiple iris waveguide bandpass filters.
- E and H plane rectangular waveguide couplers - Figure 3.
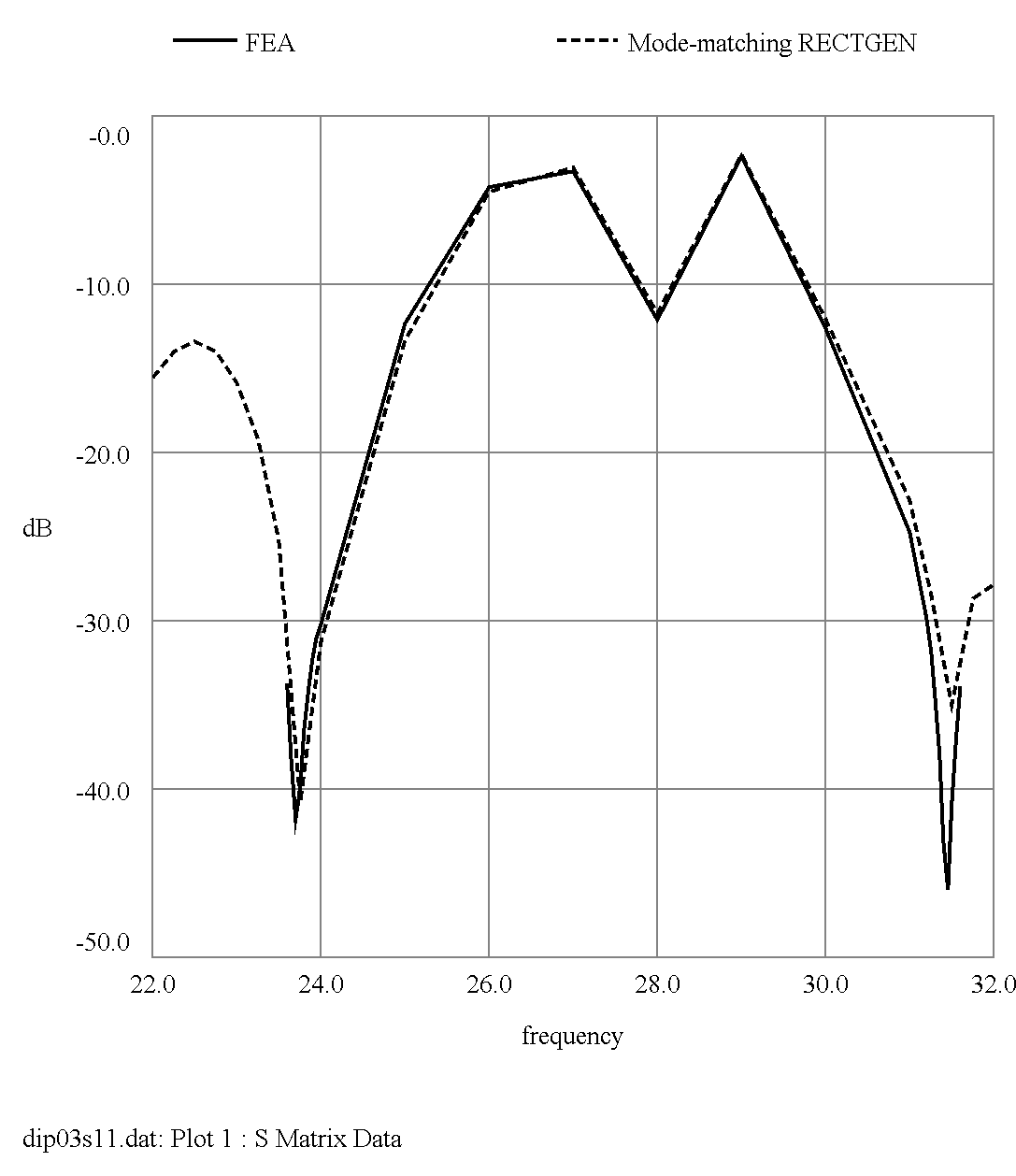
- Diplexers - Figure 4 and Figure 5
- Four horn monopulse radiator.
- Small waveguide networks and horn arrays
- Single and double ridged waveguide tapers and step transformers.
- Evanescent mode filters.
- Septum polarisers (single or dual input ports) - Figure 2
FIGURE 1 Sample Geometries from RECTGEN
Modelling Method Used By RECTGEN
The mathematical basis of the analysis program exploits a modal matching technique. The structure to be analysed must be modelled as a number of discrete rectangular or ridged waveguide segments supporting propagating as well as evanescent modes. Multiple waveguide aperture segments can coexist side by side. This flexibility extends the scope of the analysis software to include many waveguide network structures. In order to achieve an optimal run-time, modes within waveguide segments can be selected in a flexible manner and various symmetry conditions can be applied.
Program Contents
The program suite RECTGEN consists of a pre and post processor program PREPGEN and analysis programs SEPSRC and RECTGEN which can be used to characterise a variety of passive rectangular and ridged waveguide structures commonly employed in microwave and millimetre wave engineering. The analysis program SEPSRC is used to calculate modal cutoff numbers of double ridged waveguides and the program RECTGEN is subsequently applied to evaluate the generalised scattering matrix of the complete waveguide or horn structure. Far-field radiation patterns based on Kirchoff-Huygens aperture integration method can also be obtained.
Input data files for RECTGEN can be prepared interactively using PREPGEN which incorporates many screen editing facilities. The wire-frame representation of the waveguide structure can be viewed and modified interactively in 3D.
RECTGEN was developed by Dr.Soe Min Tun of S.M.T. Consultancies Ltd.
Examples
Here is an E-plane metal insert filter, analysed with RECTGEN.
Platforms
RECTGEN is available on these platforms.
References
- Alessandri F, Bartolucci, G and Sorrentino A, Admittance Matrix Formulation of Waveguide Discontinuity Problems: Computer Aided Design of Branch-line Couplers, Trans IEEE on Microwave Theory and Tech, MTT-36, No 2, 1988, p394-403
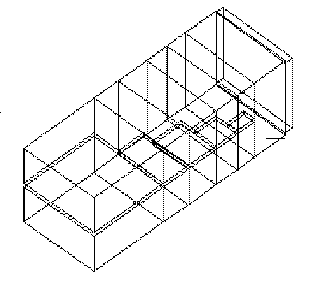 Geometry of Septum Polariser |
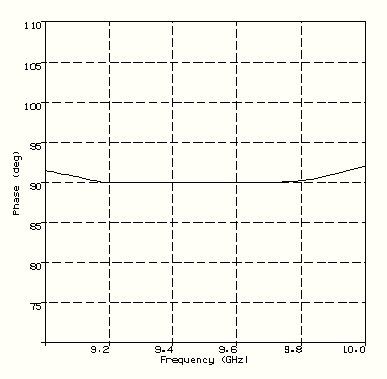 Differential Phase Performance of a Dual Port Septum Polariser |
FIGURE 2
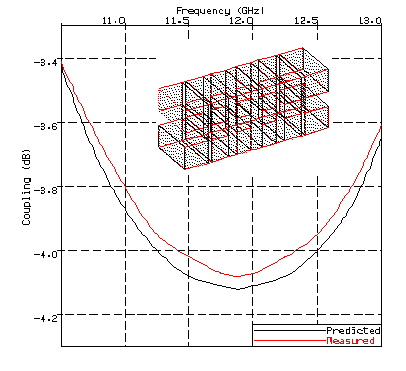 FIGURE 3 Predicted (RECTGEN) and Measured Coupling Response of a Waveguide Hybrid Coupler. Measured results from [1]. |
 FIGURE 4 Geometry of Diplexer |
 Return Loss |
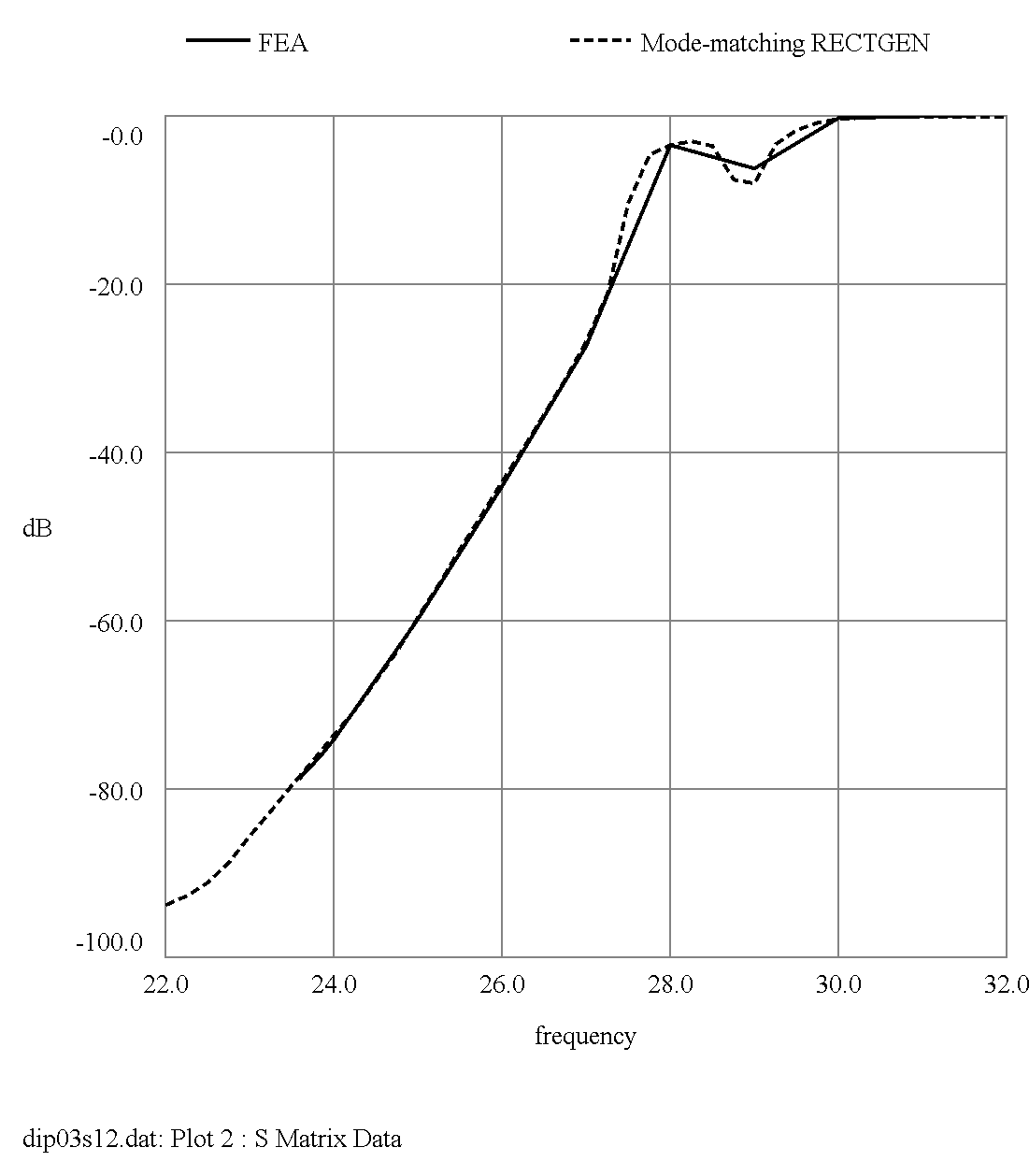 Transmission Loss |
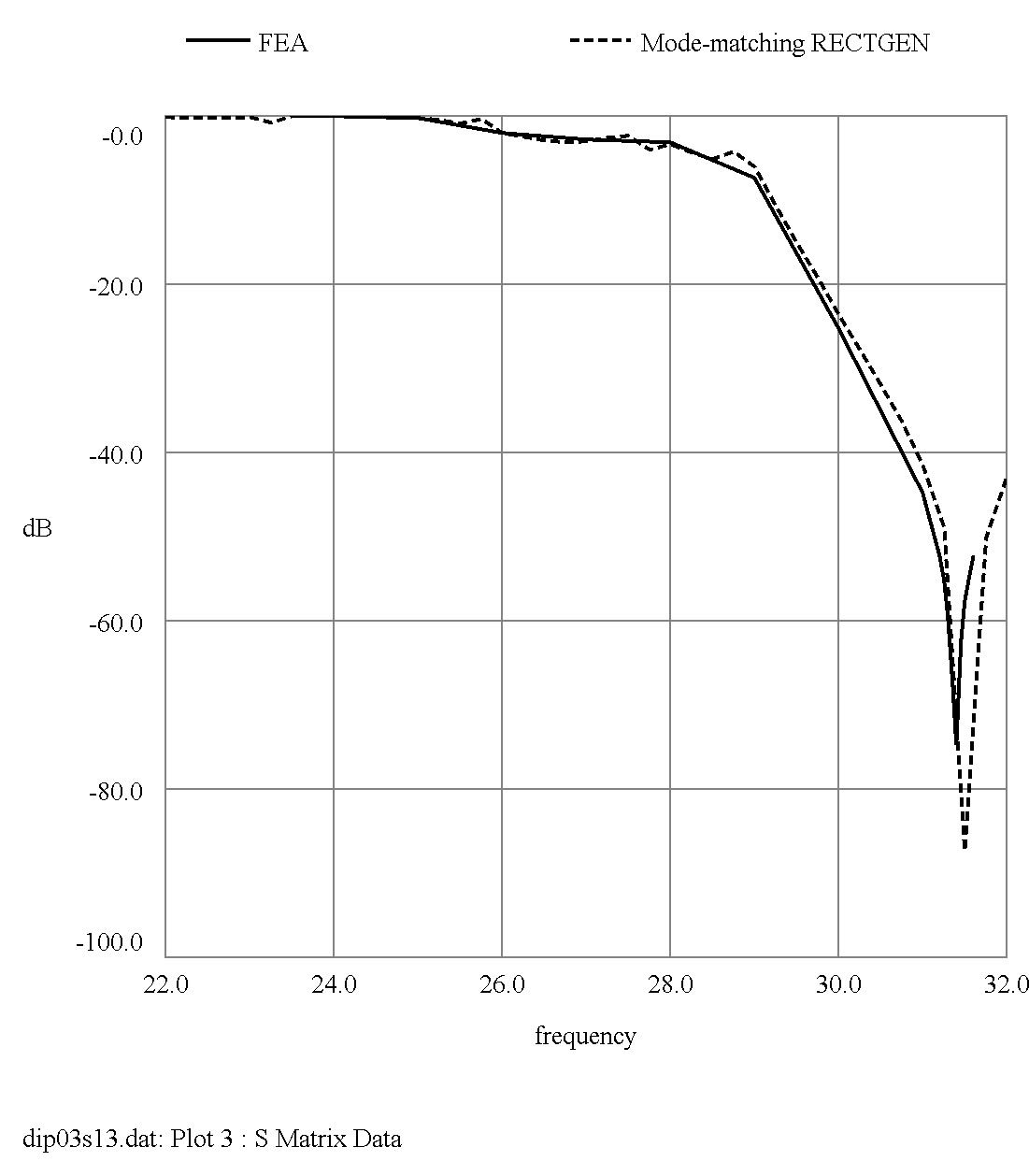 Transmission Loss |
FIGURE 5 Comparison of RECTGEN prediction (dashed) with Finite Element Analysis prediction (solid)